Early Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy Can Save Your Sight in Nigeria
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is one of the leading causes of blindness among adults globally, particularly affecting those with long-standing diabetes. In Nigeria, where diabetes prevalence is on the rise, early detection and management of diabetic retinopathy are critical to preventing vision loss and improving quality of life. This article delves into the importance of early detection, the current state of diabetic retinopathy in Nigeria, and the strategies that can be employed to mitigate this growing public health concern.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes complication that affects the eyes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. These blood vessels can swell, leak, or close, leading to impaired vision and potentially blindness if not treated timely.
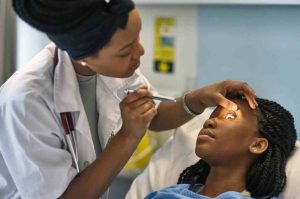
The Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Nigeria
The prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in Nigeria is alarmingly high. A systematic review and meta-analysis found that the pooled prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in Nigeria was 21.3%. This indicates that nearly one in five individuals with diabetes is affected by this condition. The increasing prevalence of diabetes, combined with limited access to healthcare, exacerbates the risk of untreated diabetic retinopathy leading to vision loss.
Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy
Several risk factors contribute to the development and progression of diabetic retinopathy. In Nigeria, the most common risk factors include:
- Duration of Diabetes: The longer a person has diabetes, the higher the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
- Poor Glycemic Control: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels significantly increase the risk of retinal damage.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure exacerbates the damage to blood vessels in the retina.
- Lack of Regular Eye Examinations: Many individuals with diabetes in Nigeria do not undergo regular eye screenings, leading to late diagnosis and treatment.

Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of diabetic retinopathy is crucial for preventing vision loss. Regular eye examinations can identify the condition in its early stages, allowing for timely intervention. Early treatment can slow or even halt the progression of the disease, preserving vision and improving quality of life.
Screening and Diagnostic Methods
Several screening and diagnostic methods are available to detect diabetic retinopathy:
- Dilated Eye Exam: An ophthalmologist dilates the pupil to examine the retina and identify any signs of damage.
- Fundus Photography: High-resolution images of the retina are taken to detect abnormalities.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): This imaging technique provides detailed cross-sectional images of the retina, allowing for early detection of diabetic retinopathy.
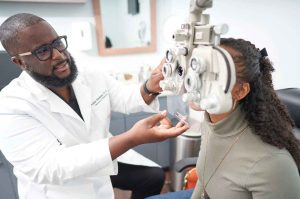
Strengthening Diabetic Retinopathy Services in Nigeria
Efforts are underway to strengthen diabetic retinopathy services in Nigeria. The DR-NET initiative aims to improve the screening and management of diabetic retinopathy from grassroots to national policy development [2]. This initiative focuses on training healthcare professionals, raising awareness, and implementing screening programs to reach underserved populations.
Case Study: Lagos University Teaching Hospital (LUTH)
Lagos University Teaching Hospital (LUTH) has been at the forefront of diabetic retinopathy screening and treatment in Nigeria. Through their dedicated DR clinic, LUTH provides comprehensive eye care services, including regular screenings, patient education, and advanced treatment options such as laser therapy and intravitreal injections. This model of care demonstrates the effectiveness of integrating diabetic retinopathy services into existing healthcare frameworks.
Challenges in Early Detection and Management
Despite the progress, several challenges hinder the early detection and management of diabetic retinopathy in Nigeria:
- Limited Access to Healthcare: Many rural areas lack adequate healthcare facilities and trained personnel to conduct regular eye screenings.
- Cost of Treatment: The cost of diagnostic tests and treatments can be prohibitive for many patients.
- Lack of Awareness: There is a general lack of awareness about diabetic retinopathy and the importance of regular eye examinations among the population.
Strategies for Improvement
To overcome these challenges, several strategies can be implemented:
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the risks of diabetic retinopathy and the importance of regular eye exams can encourage more people to seek early detection and treatment.
- Training Healthcare Professionals: Increasing the number of trained ophthalmologists and optometrists in rural areas can improve access to care.
- Government and NGO Partnerships: Collaboration between the government and non-governmental organizations can enhance the reach and effectiveness of screening programs.
- Subsidized Healthcare Services: Providing subsidized or free eye care services for diabetic patients can reduce the financial burden and encourage regular screenings.

The Role of Technology in Early Detection
Advancements in technology can play a significant role in the early detection of diabetic retinopathy. Mobile health (mHealth) solutions, such as smartphone-based retinal imaging and telemedicine, can bring screening services to remote areas. These technologies enable healthcare providers to conduct screenings and consultations virtually, reducing the need for patients to travel long distances.
Real-Time Example: Telemedicine in Rural Nigeria
In rural Nigeria, telemedicine has shown promise in improving access to diabetic retinopathy screening. Through partnerships with local health centers, telemedicine programs provide retinal imaging services that are reviewed by specialists remotely. This approach not only increases the reach of screening programs but also ensures timely diagnosis and referral for treatment.

Global Perspectives and Best Practices
Learning from global perspectives can help improve diabetic retinopathy services in Nigeria. Countries like the UK and India have implemented successful screening programs that can serve as models. For instance, the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) Diabetic Eye Screening Program has achieved significant success in reducing the incidence of severe diabetic retinopathy through systematic screening and timely treatment.
Future Directions
The future of diabetic retinopathy management in Nigeria lies in integrating comprehensive eye care services into the primary healthcare system. By leveraging technology, enhancing public-private partnerships, and focusing on capacity building, Nigeria can develop a sustainable model for early detection and treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
Conclusion
Early detection of diabetic retinopathy is crucial to saving sight and improving the quality of life for individuals with diabetes in Nigeria. While challenges exist, concerted efforts by the government, healthcare providers, and communities can significantly improve the landscape of diabetic retinopathy care. By raising awareness, increasing access to screenings, and leveraging technology, Nigeria can reduce the burden of diabetic retinopathy and ensure a brighter future for its citizens.






























 IK
IK
